When NASA’s Perseverance rover lands on Mars this afternoon, the robotic will owe its safe passage to one of the most not likely parts of technologies made considering the fact that the dawn of the House Age: the Skycrane. This seemingly sci-fi system sees the rover perilously dangle beneath a hovering rocket-driven spacecraft in advance of getting carefully reduced to the ground (consider Tom Cruise dropping from the ceiling in Mission Not possible).
Even though after thought of an unrealistic alternative to the problem of landing significant craft on other worlds, right now, engineers are assured the odd tech operates. NASA has now correctly deployed it after. In 2012, the Skycrane properly established down the Mars Curiosity rover on the Purple Planet. But when engineers first cooked up the notion approximately 20 decades back, several had been bought on it.
The Skycrane was the consequence of contemplating — and then ruling out — each individual other possibility engineers could consider of to land hefty rovers. And even though the math checked out, there was no way to really examination it on Earth. So, engineers had been left trusting a multi-billion greenback rover to a system that looked so bizarre and complicated even the NASA administrator in demand at the time termed it outrageous.
“We talked about it to no end. If this failed to go right, there would be nowhere to hide simply because each individual joe 6-pack on the avenue would be indicating that they understood it would not do the job,” Adam Steltzner of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, main engineer for the Perseverance rover, tells Astronomy. His workforce dreamed up the Skycrane maneuver, and he was liable for generating confident it worked with Curiosity.
And even though the system executed flawlessly in 2012, Steltzner and his workforce are not using anything at all for granted this time all over.
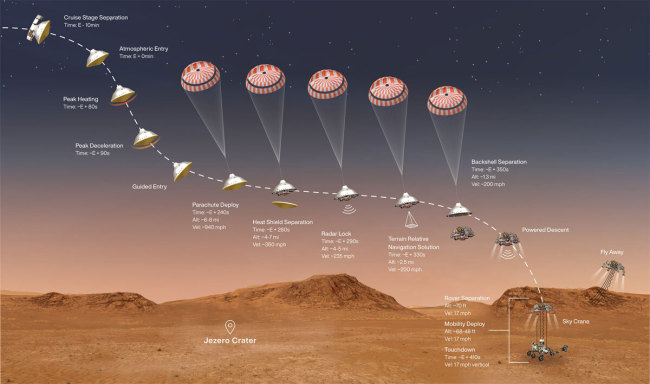
Landing on Mars calls for a difficult established of maneuvers. In the last phase, the Skycrane need to deposit the rover on the Martian surface area in advance of zooming off. (Credit rating: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
‘Seven Minutes of Terror’
When the Mars Perseverance rover hits the Purple Planet’s atmosphere right now, it will be touring at a lot more than 10,000 miles for every hour. Which is so rapidly that the rover would vaporize like a meteor if it weren’t properly tucked inside a heat-resistant, carbon fiber capsule that can withstanding temperatures up to a whopping one,600 levels Fahrenheit.
These intense temps are only the first problem Perseverance will encounter for the duration of its demise-defying plunge. Next, it requirements to deploy its massive supersonic parachute. However Perseverance’s parachute can only gradual the craft to about 200 miles for every hour. And if it landed at that speed, the rover would make a approximately $3-billion crater.
Mars’ atmosphere is dense sufficient to pose important problems for engineers, but it is nevertheless way too slender for parachutes to fully gradual down a plummeting lander. That’s why you will need an added phase of the landing sequence that can help soften the rover’s touchdown. Steltzner likes to joke that it is not the slide that kills you, it is the landing.
Making matters even worse, Mars is so far absent from Earth that NASA simply cannot communicate with the spacecraft in actual-time. Perseverance has to information by itself. By the time the spacecraft engineers again on Earth learn what’s occurred, the rover will now have been lifeless or alive on Mars for 7 minutes. NASA calls it the “seven minutes of terror.”

NASA’s first a few Mars rovers touched down inside protecting airbags, which bounced together the surface area. (Credit rating: NASA)
Mars Rovers: From Airbags to Skycranes
And which is why engineers have regularly arrive up with ingenious techniques for touching down on Mars. No one, or even two, alternatives can attain the career.
The Viking landers used equally parachutes and descent rockets to gradual the spacecraft down just in advance of landing, then the lander’s legs served as shock absorbers. Plus, Viking’s mission planners had to layout unique “showerhead” fashion rockets to steer clear of cooking the grime beneath the spacecraft, which would have killed any likely symptoms of lifetime they had been wanting for.
But when NASA started off sending rovers to Mars, it quickly understood Viking’s techniques wouldn’t do the job. If the retro rockets fired way too near to Mars’ dusty surface area, they could fling rocks and particles again on to a fragile rover’s instruments and photo voltaic panels, placing it in threat.
That’s why NASA wrapped the Mars Exploration Rovers — Spirit and Opportunity — in airbags. Those people airbags allow the rovers properly bounce together Mars’ surface area until eventually they drop their last bit of momentum. Like the Skycrane maneuver, this daring notion was audio in idea, but appeared outrageous at the time.
And in the decades in advance of the Mars Exploration Rovers had been established to get there at the Purple Planet, the world’s area companies got a collection of painful reminders on the perils of interplanetary area vacation. (Go through a lot more: The ‘Mars Underground’: How a Rag-Tag Team of Pupils Served Spark a Return to the Purple Planet.) Russia, Japan, The European House Agency and the United Kingdom all noticed missions fall short at Mars. And NASA by itself suffered again-to-again significant-profile failures at Mars to round out the nineties: the Mars Local climate Orbiter burned up on entry and the Mars Polar Lander was destroyed for the duration of its landing.
At the convert of the millennium, NASA was keen on obtaining a gain. And in 2003, its engineers shipped two profitable landings — the Spirit and Opportunity rovers — utilizing the audacious airbag system.
“We caught two landings on the Mars Exploration Rovers, and when we got accomplished with that we had been very arrogant little ones,” Steltzner recollects. With people successes in the bag, Steltzner and the other NASA engineers operating on entry, descent and landing had been using significant.

NASA’s Curiosity rover descends toward the Purple Planet as seen from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2012. (Credit rating: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona)
And as they looked ahead to what would at some point grow to be the Mars Curiosity rover — a rover the measurement of a little vehicle — they had to rethink the greatest methods to land on Mars. Their math showed airbags wouldn’t do the job the rover was way too beefy. There’s no acknowledged elements sturdy sufficient to tackle Curiosity’s weight if they utilized airbags like the types used on Spirit and Opportunity. The tech simply could not scale.
An option tactic would be to land the rover inside a system, then have it drive off, as the small Sojourner rover did in 1996. But that solution also approximately killed Sojourner. And, as NASA acquired with the Mars Polar Lander, relying on legs provides its very own problems. The ill-fated Polar Lander probably died simply because the spacecraft misinterpreted vibrations in its legs.
So, way again in the early 2000s, NASA’s engineers determined to brainstorm and set collectively a checklist of each individual single notion they could arrive up with for landing a hefty rover on Mars. They went by way of them one at a time, ruling each one out for one explanation or yet another. And which is how Curiosity finished up with the Skycrane — very little else appeared as probably to realize success. It proved to be the the very least outrageous notion.

An artist’s perception of the Perseverance Rover on Mars. (Credit rating: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Curiosity Skycrane: “The Correct Variety of Crazy”
The Skycrane operates substantially like a hefty-lift helicopter (without the need of the blades), utilizing tether cables to lessen the rover down to the surface area even though the crane relies on rocket propulsion to hover earlier mentioned. In fact, the workforce even consulted with the engineers and pilots behind the Sikorsky Skycrane, a helicopter that takes advantage of very equivalent procedure to haul logs from forests, as very well as other hefty cargo. But contrary to earthly helicopters, as quickly as the rover’s wheels strike Mars regolith, the flying crane shoots by itself clear of the landing spot, completing its process in a fiery explosion.
However, there was no way on Earth to examination how the rocket-driven Skycrane would carry out on Mars. Engineers could run simulations and validate their calculations time and again. But they could never know for confident if Curiosity would actually survive the daring maneuver. And that’s what produced it such a difficult market, even inside NASA.
At one level, the agency’s then-administrator, Mike Griffin, invited Steltzner to NASA headquarters to give a discuss to managers from area facilities all over the country. As Steltzner stood at the lectern, Griffin walked in late wearing a turtleneck and double-breasted fit, then turned and tackled the viewers. “When I listened to what these guys are executing, I reported to myself, these guys are outrageous,” Griffen reported, according to Steltzner. “So, I requested them to arrive here and demonstrate what they’re executing.”
Immediately after Steltzner wrapped up his discuss, the administrator and the engineer put in some time arguing again and forth in advance of Griffin provided up: “I nevertheless consider it is outrageous, but it could be outrageous sufficient to do the job. It could be the right variety of outrageous.”
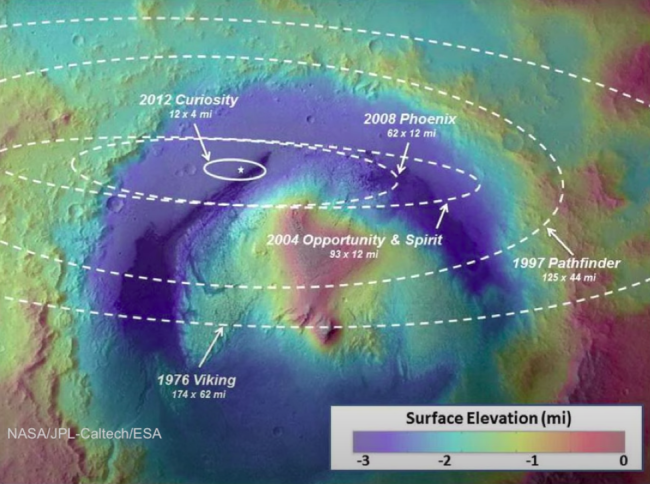
Planned landing ellipses of prior Mars rovers. Notice how substantially lesser Curiosity’s landing zone is — thanks to the Skycrane maneuver — compared to prior rovers.(Credit rating: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESA)
The Skycrane Gets NASA’s Norm
According to Steltzner, the all round skepticism surrounding the Skycrane notably adjusted following his discuss at NASA headquarters. Previously, other engineers and area facilities had been hesitant to seriously support the wild notion. But with the administrator’s reviews, that reluctance light absent. And as planning for the Curiosity mission pushed forward, NASA threw its whole assistance behind the work, Skycrane provided.
“If you are landing a rover on Mars, there is no doubt this is the right way,” Steltzner claims.
The rovers are developed to tackle rough terrain. So, when the Skycrane drops it off at speed, it is not appreciably unique than stumbling off a significant rock. In fact, equally Curiosity and Perseverance are difficult sufficient that they could survive even if the Skycrane dropped them right on best of a little boulder. The Skycrane allow NASA’s robotics engineers layout a rover that could navigate the surface area without the need of worrying about acquiring to make compromises just for its landing.
The procedure has also tested to pair nicely with radar sensors that allow the spacecraft notice its environment and autonomously information by itself to a safe spot. This permitted the Curiosity rover to strike a rather small landing focus on on Mars, and Perseverance will use a equivalent — however even a lot more specific — solution.
But according to Steltzner, that isn’t going to signify the 7 minutes of terror will be any a lot less terrifying this time all over.
“Last time, we undoubtedly had issues about whether or not this seriously was a outrageous issue to try out to do,” he claims. “Had we missed a major issue? Was it fully mistaken? Did all the parts actually arrive collectively and do the job? We answered people issues, but there are nevertheless hundreds of countless numbers of details you have to get right to make them do the job again. Our career is to make it do the job this time. I will be frightened all the way.”
