When it comes to the subject of microfibers, researchers no for a longer time will need to “break the ice.” Many thanks to a new discovery in nanomaterials, they can now bend it in its place.
“Our group experienced been doing the job on silica microfibers for 20 many years,” says Xin Guo, an optical scientist at Zhejiang University in China and just one of the authors of a research released in Science this summer season. Now, her group has become the very first to mature microfibers with flexible ice that can bend back on by themselves — devoid of fracturing.
Ice is known for remaining a brittle material, largely because of to imperfections in the framework of its crystals. But experts even now never fully recognize what‘s taking place on a molecular degree when ice variations to water and vice versa. The optical houses of the new, extremely-elastic ice microfibers could expose new insights.
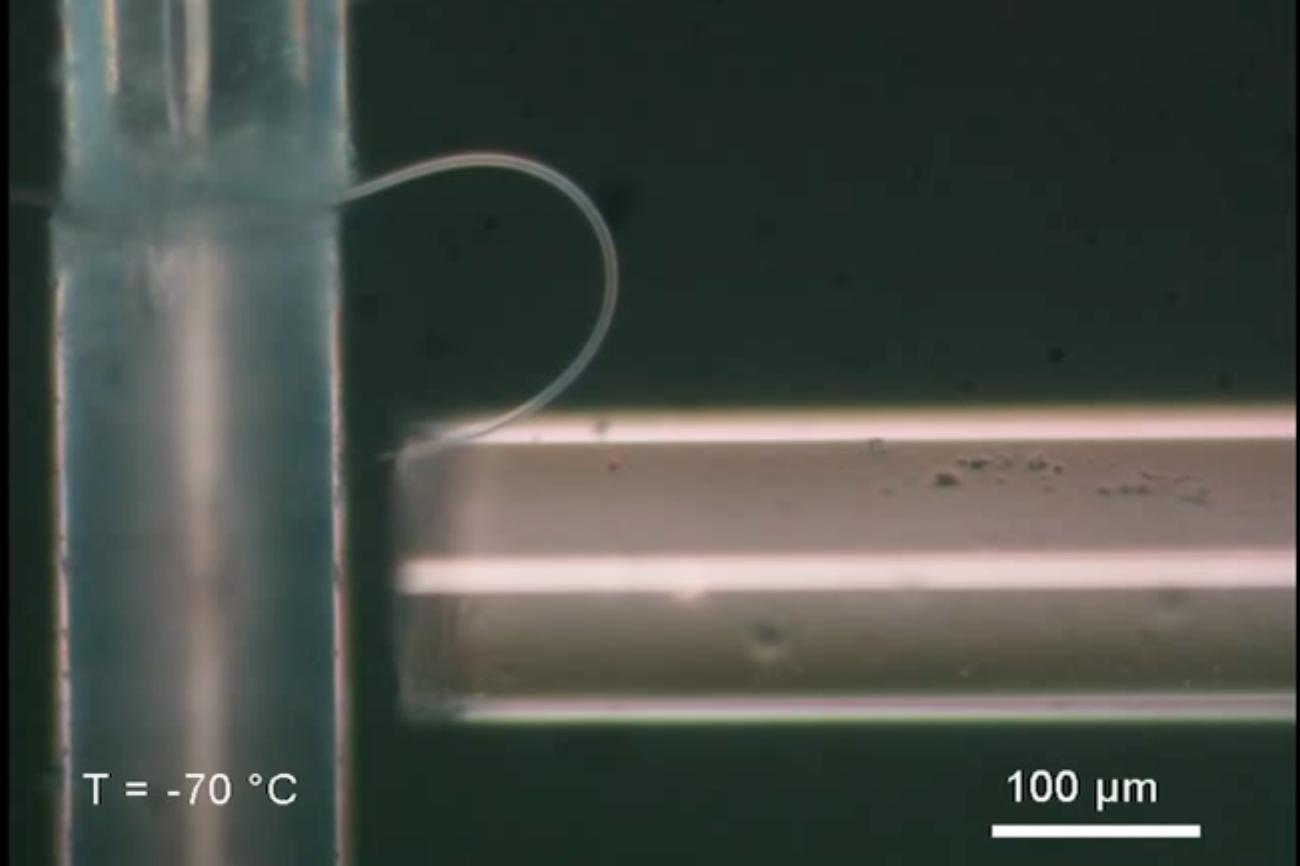
The researchers created the microfibers by cooling down a tungsten needle (which narrows to the thickness of a single atom and is the sharpest object ever produced) in a specific chamber to about –60 levels Fahrenheit, Guo says. That’s colder than any other former experiment of this nature. The group then used an electric area to draw water vapor to the needle suggestion. As the vapor froze there, it shaped a microfiber about five micrometers in diameter and about 1 millimeter in size.
“It’s very slim and very limited,” says Limin Tong, also an optical scientist at Zhejiang University and a co-author of the research. Guo adds that the fiber was shaped with single crystal ice. “We fabricated [a] higher-excellent ice microfiber with a uniform framework,” she says.
The researchers then reduced the temperature even extra, to involving –94 levels and –238 levels Fahrenheit. When they attempted to bend it, they discovered their experiment experienced worked. The resulting fiber could bend up to a utmost strain of 10.nine per cent — substantially extra than regular ice and near to the fifteen per cent theoretical utmost elasticity of ice, even though no person has ever obtained any where near to that. It also bounces back to its unique variety.
“It’s just like some magic,” Tong says of the original try to bend the substance. “Normally we never have best ice crystals. Now we have a sort of microfiber with a very uniform character.”
Whilst “cool” in and of alone, bendable ice can also be helpful. The researchers sent light-weight by the ice microfiber, which is very clear, and discovered that it worked just as well as the silica fibers typically used to transmit facts by using light-weight. Guo and Tong believe these varieties of fibers might also discover use in detecting viruses or other microbes by positioning very small organisms on the microfibers and guiding light-weight by them, we could understand extra about the concentration, density or forms of microbes that might be current.
In the upcoming, the group will also function on developing sensors that are appropriate with the bendy ice. Of training course, this fiber melts at around 14 levels Fahrenheit — that means it might not be helpful in a lot of conditions. “That is a very typically used temperature in laboratories,” Tong says, “and also in some varieties of ice cream.” But researchers in the polar areas, or in area, could make use of them because of to the inherently minimal temperatures.
Potentially most importantly, light-weight shined by these frozen fibers could aid researchers research what occurs when ice variations phases. Since a section alter can be brought about just by bending the microfiber, performing so could expose extra about how ice crystals variety, why they variety the way they do and what molecules are involved.
For now, the up coming move is to decide if for a longer time ice microfibers can be created. “We have a lot of mysteries that are even now not known to us as experts,” Tong says.




