To glean insights into weather adjust, a compact clan of intrepid experts deploys to some of the most excessive sites on Earth: the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets.
From temporary camps, they drill prolonged cores of ice made up of chemical clues about ancient climates — clues that have unveiled vital insights into how spaceship Earth’s climatic lifestyle assistance procedure will work.
Like other users of the ice-coring clan, Dorthe Dahl-Jensen, hopes this knowledge can finally support tell decisions vital to averting the worst feasible outcomes of human-triggered weather adjust.
Indicating the globe is heading less than is dangerous due to the fact young persons will say, ‘Why must I get an education, there is no potential for me in any case.’ That has hardly ever been extra erroneous. A lot of persons have revealed that we can address this problem.” — Dorthe Dahl-Jensen
Dahl-Jensen is a researcher at the University of Manitoba’s Centre for Earth Observation Science, and a Professor at the Niels Bohr Institute, the University of Copenhagen. She was recently awarded the Mohn Prize, a prestigious honor for excellence in Arctic exploration.
I sat down to chat with Dahl-Jensen at the new Arctic Frontiers conference in Tromsø, Norway, in which she gained the award. Signing up for me was a close friend and fellow science journalist, Tomasz Ulanowski, a reporter for the Polish publication Gazeta Wyborcza. We each posed concerns to her about what experts are finding out from studying ice. What follows is a combine of concerns and responses interwoven with track record info from my have reporting.
Make absolutely sure to read by to the close, in which Dahl-Jensen moves beyond the science to address what she thinks it is stating about the urgent want to act on weather adjust. Contrary to what we generally hear, it is not essentially a depressing or even terrifying concept.
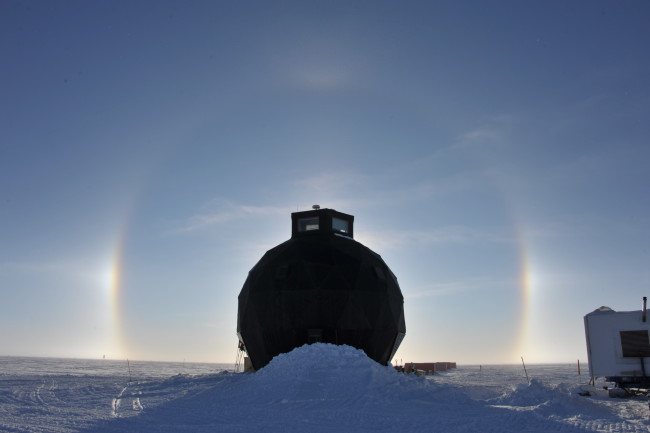

A dome framework is the centre of lifestyle at the East Greenland Ice-main Task, or Eastgrip. Users of the ice coring group get their foods and loosen up within. Experts hope the job will strengthen knowing of how ice streams will contribute to potential sea-level adjust, and also expose new aspects about previous climatic problems. (Source: East Greenland Ice-main Task, www.eastgrip.org)
My colleague obtained factors heading with this dilemma: What does the ice teach us?
She commenced by noting just how unusual drinking water ice is: “Ice is lighter than drinking water,” she claimed. “There are not quite a few other supplies in which the stable sort is lighter than the liquid sort. So it floats on the drinking water.”
That may not sound so unique, but ice floating on drinking water somewhat than sinking essentially has a profound influence: It assists control our planet’s weather.
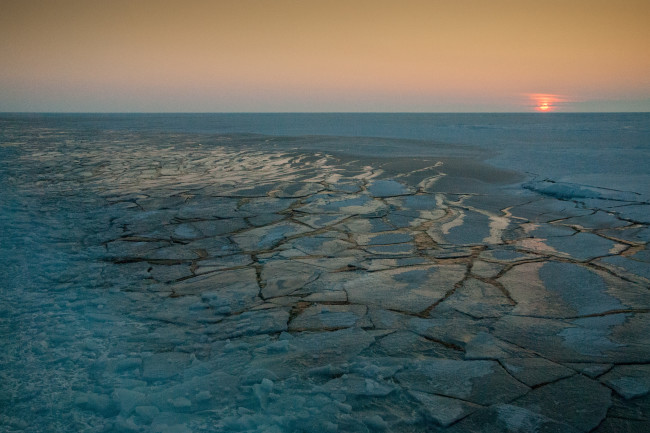

The sun sets above the Arctic sea ice pack, as noticed in October of 2014. Sea ice assists manage chilly temperatures in the Arctic. (Source: NASA/Alek Petty)
Which is due to the fact floating sea ice varieties a dazzling protect above the Arctic Ocean and bordering waters. That protect displays massive amounts of photo voltaic vitality back into room — vitality that usually would warm the location. This assists manage frigid problems in the higher north.
But human-triggered warming has triggered this reflective protect of floating sea ice to shrink at a amount of 12.85 percent per ten years considering that 1979, as calculated each September. (This is when the ice reaches its yearly lowest extent at the close of summer time.) Reports counsel that considering that the late 20th century, the drop in summer time Arctic sea ice has been steeper than at any time in the previous one,450 yrs.
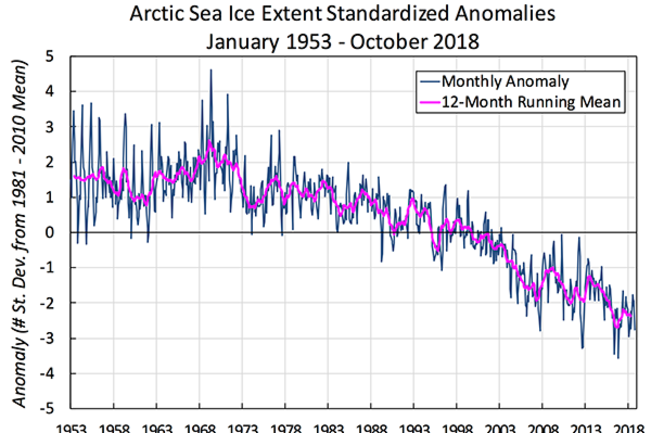
This graph exhibits how the extent of Arctic sea ice has departed from regular signifies concerning January 1953 and December 1979. For January 1979 to the existing, knowledge have been derived from satellite sensors. The document prior to 1979 is primarily based on operational ice charts and other sources. (Image by Walt Meier and Julienne Stroeve, Nationwide Snow and Ice Data Center, University of Colorado, Boulder.)
As sea ice shrivels, extra and extra photo voltaic vitality is currently being absorbed by the comparatively darkish ocean area somewhat than currently being mirrored back to room. The consequence: The Arctic has warmed twice as a great deal as any other location on Earth, a phenomenon experts simply call “Arctic amplification.”
The actuality that ice floats on the area of the sea also will make it “super elementary — due to the fact it shields the lifestyle in the ocean,” Dahl-Jensen told us.
At the base of life’s meals web in Arctic waters are phytoplankton. As winter season turns to spring and temperatures normally warm, sea ice thins, breaks up and and last but not least melts, furnishing phytoplankton with the photo voltaic vitality they want to increase. Springtime blooms of phytoplankton are grazed on by animals known as zooplankton. Arctic species are comparatively significant and fatty, furnishing the Arctic cod that feed on them a good deal of vitality per bite. The cod are in flip eaten by seals, which are the beloved food of polar bears.
As the Arctic has warmed, the protect of sea ice has thinned and damaged up earlier, in flip resulting in earlier blooms of phytoplankton. This is sending impacts rippling up the Arctic marine meals web. For illustration, there is proof that the Arctic zooplankton are currently being replaced by extra southerly, significantly less nutritious species. And extra southerly fish species seem to be migrating northward.
Thinning sea ice has allowed extra daylight to get to the drinking water proper beneath the ice, triggering blooms of phytoplankton earlier than in the previous.
Experts say that a massive change in Arctic marine ecosystems may perhaps be in the offing, but they are not still absolutely sure what the end result will be. As Dorothy Dankel, a fisheries scientist at Norway’s University of Bergen, set it to me for a element story I wrote not prolonged back, “It’s a fascinating, intricate, ideal storm. It can possibly appear out genuinely terrific, or anything could go down the shithole.”
Shifting to a different aspect of Arctic ice in the course of our interview with Dahl-Jensen, my colleague questioned this: What can it teach us about Earth’s record?
Dahl-Jensen has prolonged examined the chemical and other clues trapped within cores of ice drilled from the Greenland ice cap in purchase to achieve insights into previous climates. The hope is that people insights can support us see better what the potential retains as we go on to pump carbon dioxide and other heat-trapping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Dahl-Jensen pointed out that each year’s snowfall on the ice cap “creates a layered document. It is extremely a great deal like tree rings,” she claimed. “You get a layer from every year.” And every once-a-year layer of snow finally compresses into ice, trapping climatic clues within it.
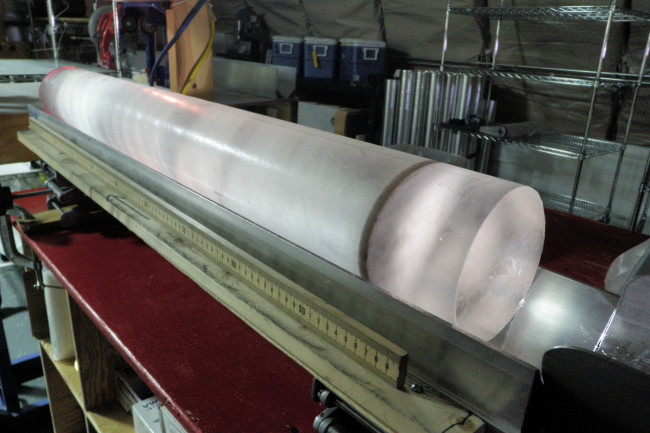

The darkish band in this layered ice main from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet Divide is volcanic ash that settled on the ice sheet about 21,000 yrs back. (Source: Heidi Roop, NSF)
“On the Greenland Ice Sheet we get weather info heading two hundred,000 yrs back in time,” she claimed. “At the bottom, we also uncover material that is one million yrs aged.”
In Antarctica, Dahl-Jensen pointed out that the layered ice document goes back extra than 800,000 yrs. “We are hoping for one.five million yrs, and we even believe that that it will have to be at minimum five million yrs in sites,” she claimed.
“We use ice as a record e book,” she claimed. “That’s what fascinates me.”
That record e book consists of info about the makeup of the atmosphere in millennia previous. When snow falls to the area and is then coated by still extra, it finally turns to ice less than the overlying strain. Air that was trapped concerning the snowflakes is then preserved, very first in bubbles and then within the matrix of ice crystals. Going back layer-by-layer, and so year-by-year, experts can recover that air and establish how a great deal carbon dioxide, methane and other gases were being existing in the previous.

Tiny bubbles of air are apparent in this sliver of Antarctic ice. Air bubbles like this offer important info about previous concentrations of greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere.(Source: CSIRO via Wikimedia Commons)
The icy record e book also consists of info about the temperatures that prevailed when the snow very first fell. This info comes in the sort of chemical fingerprints corresponding to warmer or cooler problems in the clouds from which the snow fell.
“We can also measure dust particles in the ice, wind-blown dust,” Dahl-Jensen claimed. “The dust we uncover in the Greenland ice cores largely comes from China. So it moves a prolonged way. And we can measure how a great deal dust is existing. This is a perform of how dry it was in China, and also a perform of how solid the storms were being that moved the dust to Greenland.”
In the close, experts can measure about “10 different parameters with once-a-year resolution. We use all these 10 parameters to day the main. So we only rely — one year, summer time and winter season, yet another year, summer time and winter season. And we can go hundreds of yrs back in time. This provides just a gold mine of weather info,” Dahle Jensen claimed.
“What we see in ice cores, and what is also supported by geological data that go further more back, is that each time we’ve experienced higher values of CO2, we’ve experienced warm temperatures,” she claimed. “So there has generally been a solid correlation concerning CO2 and area temperature. It is surprising that persons can question no matter whether the higher values of greenhouse gases now will consequence in warmer temperatures as soon as our procedure adjusts to the vastly transforming values.”
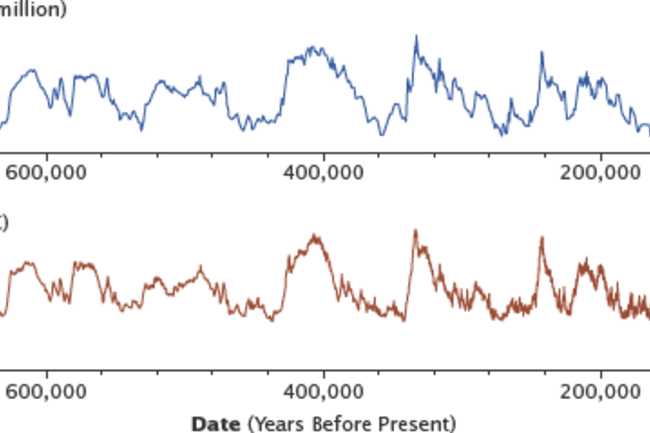
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has corresponded carefully with temperature above the previous 800,000 yrs, as seen in these knowledge from the EPICA ice main drilled from Antarctica. Though the temperature improvements were being touched off by versions in Earth’s orbit, the amplified worldwide temperatures released CO2 into the atmosphere, which in flip warmed the Earth. (Source: NASA Earth Observatory.)
Dahl-Jensen is finding at an aspect of weather adjust that is not greatly appreciated. Indeed, worldwide common temperature has currently risen by about one diploma C thanks to emissions of greenhouse gases so far. But if we were being to shut off emissions tomorrow, we would not forestall further more warming absolutely. Much from it, in actuality. We’d even now see a great deal extra warming.
Which is due to the fact the oceans, which have been absorbing extra than ninety percent of the heat that has developed up, develop a good deal of inertia in the weather procedure. This stems from two actual physical points: It usually takes a prolonged time for heat to completely warm the oceans, and also a prolonged time for that heat to appear out and warm air temperatures.
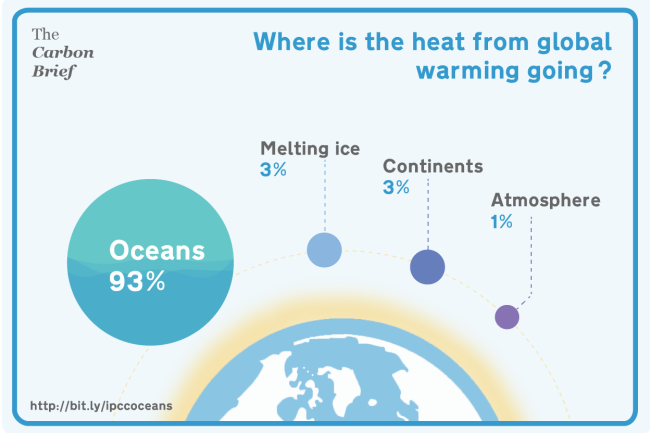
Source: Rosamund Pearce, Carbon Quick: https://www.carbonbrief.org/heat-absorbed-by-oceans-has-doubled-considering that-1997)
Here’s how Dahl-Jensen spelled out it:
“We have a procedure that is fully out of equilibrium now. The procedure does not respond from day to day. The area of the sea does, but the ocean as a total does not. Which is due to the fact warming the deep ocean usually takes spot on the scale of a thousand yrs. So we have a procedure that usually takes a thousand yrs to get into equilibrium. And that signifies we have a strongly imbalanced procedure now. As a consequence we haven’t seen the warming you’d hope from the CO2 we have currently set in the atmosphere.”
How a great deal added warming can we hope?
“I would say two degrees,” Dahl-Jensen claimed. “But I would not listen to that if I were being you, due to the fact there are so quite a few factors we do not know.”
Among the them: aspects about what happens to carbon that gets absorbed into the ocean.
“The carbon cycle is most likely one of the most complicated balances to make,” Dahl-Jensen claimed. “How does the ocean do this uptake?” Thanks to absorption of carbon dioxide into ocean waters, “we see that the ocean is getting extra acid. This cuts down its skill to get up extra CO2.”
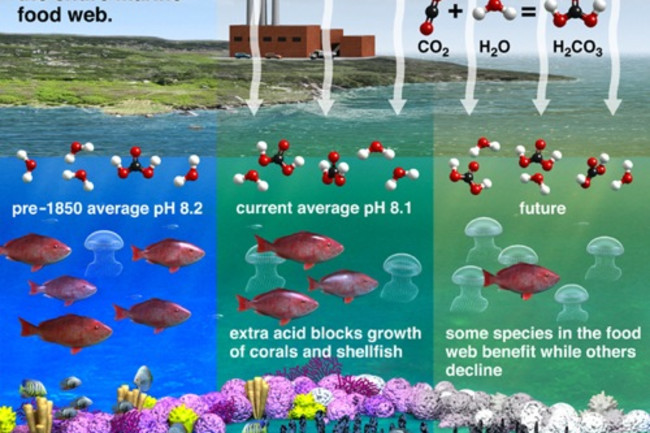
About 50 percent of the CO2 that has been pumped into the atmosphere considering that the dawn of the industrial period has been absorbed by the oceans by organic processes, generating them extra acidic. This harms marine ecosystems, which include coral reefs. (Source: John MacNeill, Weather Central: https://www.climatecentral.org/gallery/graphics/ocean-acidification-process)
In other phrases, the ocean has been performing us a favor by absorbing CO2 that usually would have warmed the world. (But we haven’t been performing the oceans and marine organisms a favor due to the fact that CO2 is resulting in acidification — see the graphic over.)
How a great deal extra can we rely on the ocean to absorb tons of CO2? Experts aren’t absolutely sure.
I then turned our discussion towards the thought of climatic tipping points. A lot of experts say we have about 10 yrs left to steer clear of crossing a catastrophic threshold. But how do we reconcile that thought with the actuality that we may perhaps have hundreds of yrs of further more warming in the pipeline no make a difference what we do?
“I really do not genuinely like this,” Dahl-Jenssen claimed. “I’m not fond of these extraordinary approaches of presenting factors . . . I feel the term tipping level is extremely generally misused, due to the fact in my impression, tipping level signifies if you reverse the process you will not get back to the identical level all over again. I feel if we reduce the CO2 we would essentially get back to the identical level all over again.”
She also claims the tipping level argument prevents persons from getting motion. “I feel it scares persons extra than it tells them that we are in a globe of options, and [weather adjust] is anything we can address. We just have to get it seriously and get cracking. We must convey to all our young persons that this is the most crucial factor in the globe, that we want a tremendous-qualified set of persons who can support us address it in the potential. I feel that would be a a great deal, a great deal extra precious level of look at than telling persons that the globe will go less than in 10 yrs.”
Youthful persons, like the Swedish weather activist, Greta Thunberg, are currently stepping up, Dahl-Jensen noticed. “They are stating, ‘Hey, appear on, go away a globe for us, we really do not have a Planet B.’ That is just incredible,” Dahl-Jensen claimed.
“But I feel stating the globe is heading less than is dangerous due to the fact young persons will say, ‘Why must I get an education, there is no potential for me in any case.’ That has hardly ever been extra erroneous. A lot of persons have revealed that we can address this problem — we can prevent the emissions of greenhouse gases, we can simply go to environmentally friendly vitality, and we can also reside with a globe that results in being warmer.”
Even so, there will be significant challenges, Dahl-Jensen acknowledged. One is that quite a few persons will have to migrate from pieces of the world that will turn out to be not possible to reside in thanks to sea level rise, soaring temperatures and other impacts.
“We have to be extra tolerant of motion of populations,” she claimed. “We cannot permit persons to go into war each time some persons have to shift . . . We have to say, ‘Yes, you’re proper, you cannot reside there, it’s underwater, or far too dry.’ We have to permit for motion.”
Dahl-Jensen pointed out that drinking water shortages assisted ignite the conflict in Syria that despatched quite a few refugees streaming into Europe. “Syria was the very first weather adjust war we’ve experienced,” she claimed.
Except we begin to strategy for the unavoidable will increase in sea level and critical heat and drought that are coming, extra wars fomented by weather adjust will be in the offing, she argued.
At the close of our discussion, Dahle-Jensen mirrored on how complicated it is for experts to support prompt optimistic motion like that.
She similar an incident in which a international minister as soon as accused her and other experts of hampering motion by not furnishing definitive responses. “‘How can you hope us to react when you say anything different each day?'” she recollects him stating. In her look at, that mirrored a elementary misunderstanding of how science essentially will work.
“We are not stating anything different each day, but we are generally upgrading our knowledge,” Dahl-Jensen told us. “So I answered him back: ‘Why didn’t you predict the economic crisis? Since you know, it’s variety of a very similar intricate procedure that persons cannot predict. ‘He obtained so furious he claimed, ‘Dorthe, I’ll hardly ever give you a grant all over again.’”
It didn’t essentially pan out that way. “He did calm down,” she claims.
