30 TB PCIe 4.0 SSDs, 20 TB HDDs push storage limits in 2020
Significant-general performance PCIe four. SSDs are soaring past 30 TB, and spinning hard drives are hitting 20 TB for a cheaper alternate to cope with the escalating growth of data as 2020 attracts to a close.
Chip companies also continued to drive the envelope with denser 3D NAND flash that can assist consumers reduce the charge per little bit and decrease their storage footprints. Micron unveiled its 176-layer 3D NAND in November at the Flash Memory Summit, while it disclosed no timeline for availability. In December, SK Hynix declared that it offered controller businesses with samples of its 176-layer, 512 Gigabit triple-level mobile (TLC) flash, which it phone calls “4D NAND.”
At year’s finish, Intel introduced PCIe four.-dependent D5-P5316 SSDs constructed with its one hundred forty four-layer quad-level mobile (QLC) 3D NAND that can store 4 bits per mobile. The D5-P5316 is due in the initially fifty percent of 2021 at capacities up to 30.seventy two TB. Previously in the calendar year, Intel extra reduce-ability single-port PCIe four. solutions, the D7-P5500 and D7-P5600, constructed with ninety six-layer TLC 3D NAND.
PCIe four. SSDs make inroads
Lower-latency enterprise PCIe four. SSDs emerged in late 2019, when Samsung unveiled its PM1733 and PM 1735, with a 30.seventy two TB model readily available upon ask for. Kioxia followed match in 2020, with its CM6 featuring up to 30.seventy two TB with single- and twin-port solutions. Samsung and Kioxia declare exams exhibit their PCIe four. SSDs hitting at minimum 1.four million IOPS for random reads and 7 GBps for sequential reads.
But Intel claimed to have the “world’s swiftest data heart SSD” with the P5800X, which it introduced this thirty day period. The P5800X takes advantage of 2nd-generation 3D XPoint memory that Intel produced with Micron to fill the hole amongst slower and considerably less-high priced NAND flash, and a lot quicker and increased-priced DRAM. Intel offered off its NAND flash business to SK Hynix in October to concentrate on AI, 5G networking, edge computing and its 3D XPoint solutions, which it makes as Optane.
Micron in late 2019 explained its initially-generation 3D XPoint-dependent X100 was the swiftest SSD, delivering 2.5 million IOPS for data reads and far more than nine GBps of study-create throughput in exams. But Intel promises the new P5800X supports PCIe four. and exams out at four.six million random-study IOPS and 7.2 GBps in sequential-study throughput to increase general performance in excess of its PCIe 3.-dependent P4800X predecessor.
Concentrate on takes advantage of for PCIe four. SSDs
PCIe four. SSDs double the bandwidth of PCIe Gen3 drives to goal the most demanding workloads, including analytics, AI, device understanding and money buying and selling programs. But they involve servers with processors that support the PCIe Gen4 technological innovation. So much, the principal selection has been servers outfitted with AMD’s Epyc CPU. Intel has yet to disclose when its server processors will support PCIe four..
Swapna Yasarapu, senior director of SSD merchandise marketing for data heart gadgets at Western Digital (WD), explained many buyers still use slower SAS and SATA SSDs, and even PCIe Gen3 SSDs can improve general performance by a multiplier of two to 5 instances. In July, WD delivered its optimum-performing generate for cloud and data heart workloads, the PCIe 3.1-dependent Ultrastar DC SN840. WD claimed the SN840 attained 780,000 IOPS for random reads and sequential throughput of 3.5 GBps for reads and 3.3 GBps for writes in exams.
Kioxia pushed the boundaries of SAS in 2020 with its new PM6 Series SSD supporting 24 Gbps technological innovation, instead than the 12 Gbps solutions available in the past. Kioxia explained buyers requested create-intense drives, so the PM6 supports ten generate writes per working day. Kioxia’s data sheets list the PM6’s sequential study general performance at far more than four.3 GBps.
64 TB SSD from Nimbus Details
At the reduce finish of the SSD general performance spectrum, Nimbus Details released SAS- and SATA-dependent 64 TB 3.5-inch SSDs that it constructed with dense QLC flash to switch HDDs. At $170 per TB, the ExaDrive NL 64 TB SSD fees far more than HDDs, but Nimbus promises buyers can understand price savings in electricity, cooling and rack place.
Other ultrahigh-ability QLC SSD solutions readily available in storage systems contain Pure Storage’s 49 TB DirectFlash modules and IBM’s 38.four TB FlashCore modules, which both of those support PCIe and NVMe for increased general performance. But as opposed to the Nimbus 64 TB ExaDrive NL SSD, the IBM and Pure flash modules are designed for use only in their storage systems.
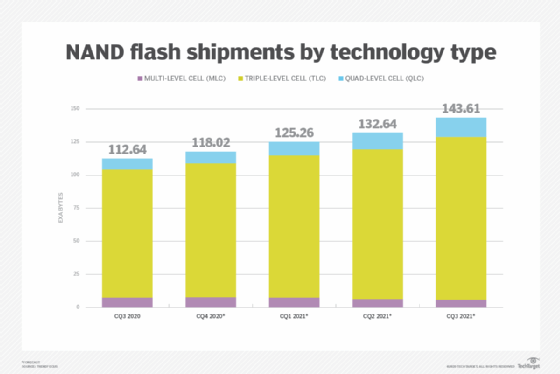
Whilst flash companies are coming out with new QLC SSDs that can assist reduce fees, the drives continue to be a lower percentage of total overall shipments. Don Jeanette, a vice president at Trendfocus, believed that QLC accounted for only 7.2{36a394957233d72e39ae9c6059652940c987f134ee85c6741bc5f1e7246491e6} of the 112.six exabytes of NAND shipments in the 3rd quarter, with TLC at 85.8{36a394957233d72e39ae9c6059652940c987f134ee85c6741bc5f1e7246491e6} and two-bits-per-mobile multi-level mobile (MLC) flash at 7.{36a394957233d72e39ae9c6059652940c987f134ee85c6741bc5f1e7246491e6}.
New form aspects also continue on to arise from SSD companies. Distributors sampling new E1.S SSDs that support the Business & Datacenter SSD Form Aspect contain Intel, Kioxia, Samsung and startup Fadu Technologies. E1.S SSDs are noticed as a substitute for gumstick-shaped M.2 SSDs that many hyperscalers use in servers, since they provide increased density and very hot-plug functionality to enable them to switch drives though the program is operating.
Computational storage drives outfitted with processors to enable compute solutions also obtained a new E1.S selection in 2020, when NGD Units extra a 12 TB SSD. But Trendfocus’ Jeanette explained he does not hope E1.S SSDs to ramp up in quantity until 2022 or 2023.
In the meantime, Western Digital innovative the Zoned Storage initiative that it introduced in 2019 with a new 2.5-inch Ultrastar DC ZN540 SSD. Zoned Namespaces SSDs create data sequentially to discrete regions of the generate to increase general performance and usable ability. Western Digital claimed its ZN540 could improve general performance by 4x and top quality of assistance by 2.5 in excess of regular SSDs. The Ultrastar SSD is sampling to find buyers, but software support for Zoned Storage is still in the growth phase.
NAND flash chip price ranges have been trending downward in the 2nd fifty percent of 2020, featuring the opportunity to also reduce fees for enterprise sound-point out drives. But SSDs still simply cannot match the price tag per GB of hard disk drives (HDDs) for enterprises and hyperscalers in want of mass storage.
All 3 HDD companies — Seagate, Toshiba and Western Digital — have worked on microwave-assisted magnetic recording (MAMR) and heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) systems to defeat the worries affiliated with recording data reliably at increasingly significant generate densities.
The new 20 TB Ultrastar DC HC650, with shingled magnetic recording, and 18 TB Ultrastar DC HC550, with regular magnetic recording, that Western Digital began shipping in 2020 use vitality-assisted MAMR recording heads. By year’s finish, Seagate began shipping 20 TB HDDs, constructed with HAMR technological innovation, to find data heart buyers.
Other new HDD systems to increase general performance at increased areal density and ability contain Western Digital’s triple phase actuator and Seagate’s MACH.2 multiactuator technological innovation.




