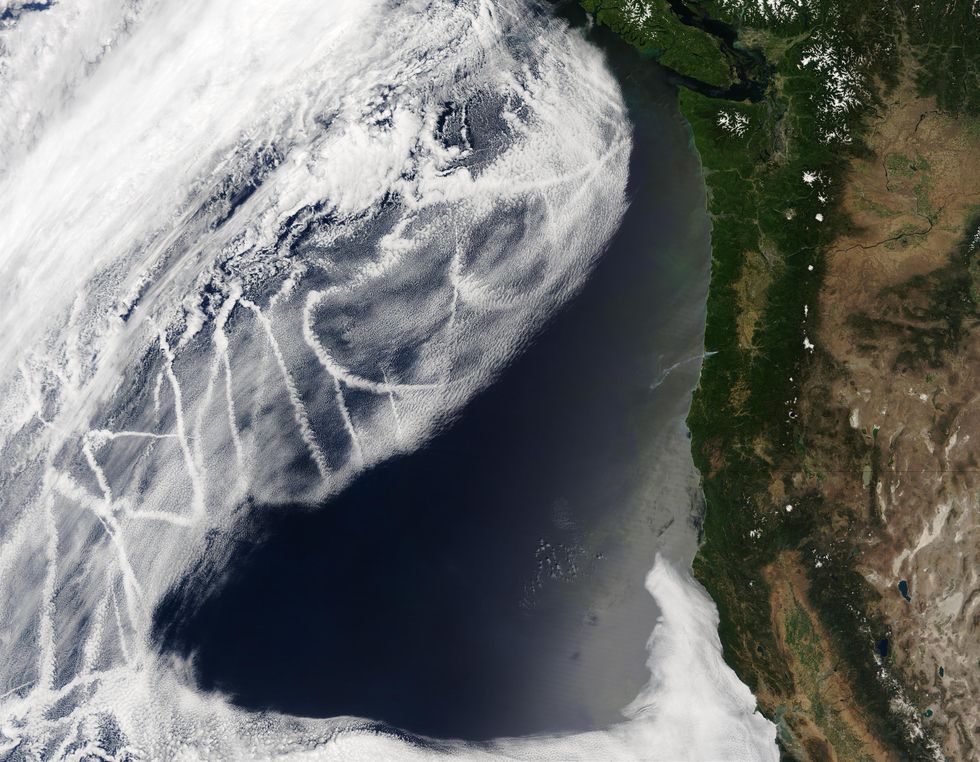
Researchers have recognized for a long time that the particulate emissions from ships can have a dramatic influence on reduced-lying stratocumulus clouds previously mentioned the ocean. In satellite illustrations or photos, pieces of the Earth’s oceans are streaked with dazzling white strips of clouds that correspond to transport lanes. These artificially brightened clouds are a consequence of the very small particles made by the ships, and they mirror far more sunlight back to place than unperturbed clouds do, and much far more than the dark blue ocean underneath. Considering that these “ship tracks” block some of the sun’s power from reaching Earth’s area, they reduce some of the warming that would otherwise happen.
The development of ship tracks is ruled by the exact same basic concepts powering all cloud development. Clouds by natural means surface when the relative humidity exceeds 100 per cent, initiating condensation in the ambiance. Individual cloud droplets kind all around microscopic particles identified as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN). Commonly speaking, an improve in CCN boosts the variety of cloud droplets when reducing their size. Through a phenomenon recognized as the
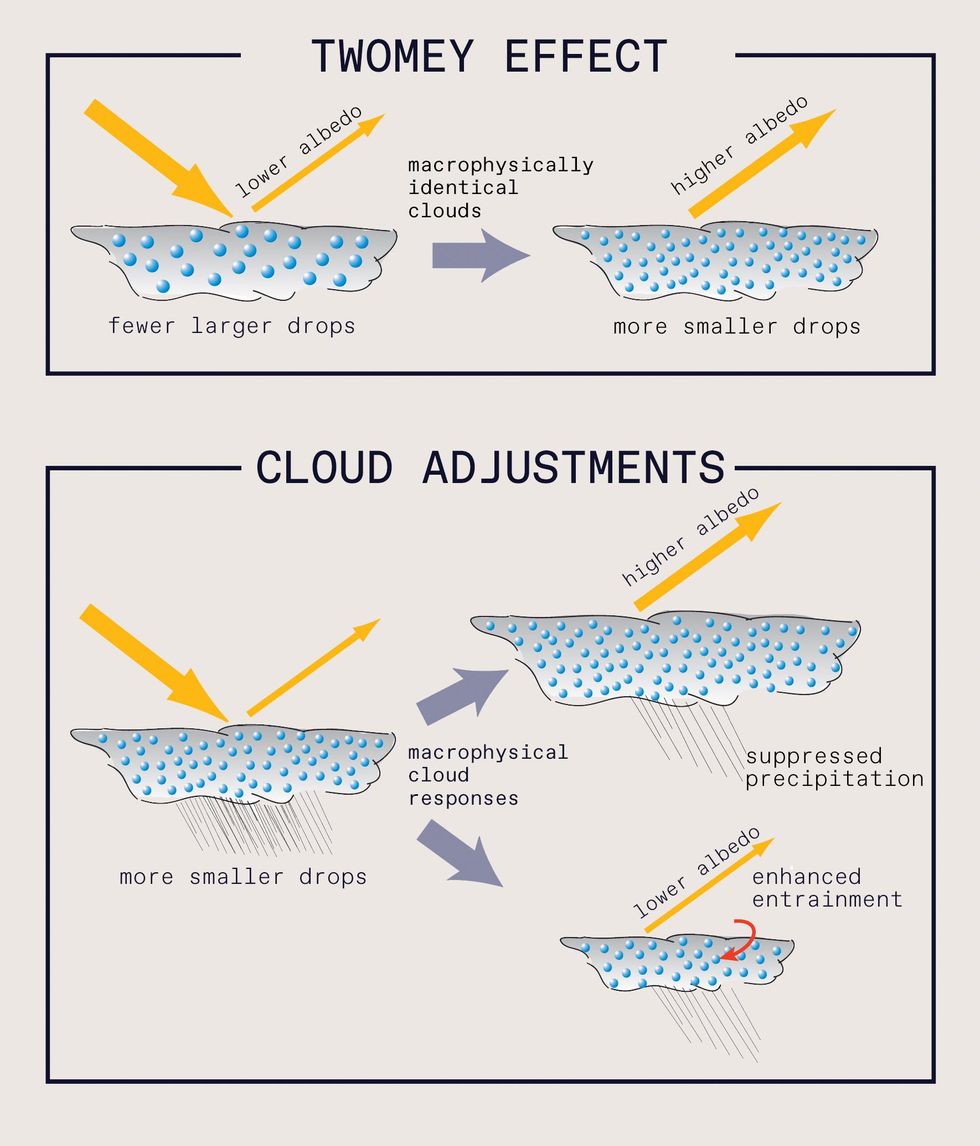
Twomey influence, this substantial concentration of droplets boosts the clouds’ reflectivity (also identified as albedo). Resources of CCN include aerosols like dust, pollen, soot, and even micro organism, alongside with gentleman-produced air pollution from factories and ships. Above remote pieces of the ocean, most CCN are of pure origin and include sea salt from crashing ocean waves.
Satellite imagery displays “ship tracks” in excess of the ocean: dazzling clouds that kind simply because of particles spewed out by ships.Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Immediate Reaction Team/GSFC/NASA
The aim of the MCB Task is to take into account whether intentionally introducing far more sea salt CCN to reduced maritime clouds would interesting the world. The CCN would be produced by spraying seawater from ships. We be expecting that the sprayed seawater would instantly dry in the air and kind very small particles of salt, which would increase to the cloud layer by means of convection and act as seeds for cloud droplets. These produced particles would be much lesser than the particles from crashing waves, so there would be only a tiny relative improve in sea salt mass in the ambiance. The aim would be to produce clouds that are marginally brighter (by 5 to 10 per cent) and quite possibly more time long lasting than normal clouds, resulting in far more sunlight getting reflected back to place.
“Solar local climate intervention“ is the umbrella time period for assignments these types of as ours that entail reflecting sunlight to cut down worldwide warming and its most perilous impacts. Other proposals include sprinkling reflective silicate beads in excess of polar ice sheets and injecting products with reflective houses, these types of as sulfates or calcium carbonate, into the stratosphere. None of the approaches in this youthful discipline are nicely comprehended, and they all have perhaps big unidentified hazards.
Solar local climate intervention is
not a substitute for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, which is critical. But these types of reductions is not going to address warming from present greenhouse gases that are by now in the ambiance. As the outcomes of local climate transform intensify and tipping points are reached, we may require choices to reduce the most catastrophic repercussions to ecosystems and human everyday living. And we are going to require a apparent knowing of equally the efficacy and hazards of solar local climate intervention systems so individuals can make educated decisions about whether to employ them.
Our team, primarily based at the
College of Washington, the Palo Alto Analysis Middle (PARC), and the Pacific Northwest Nationwide Laboratory, comprises specialists in local climate modeling, aerosol-cloud interactions, fluid dynamics, and spray units. We see quite a few important strengths to maritime cloud brightening in excess of other proposed kinds of solar local climate intervention. Employing seawater to produce the particles provides us a totally free, considerable supply of environmentally benign materials, most of which would be returned to the ocean by deposition. Also, MCB could be finished from sea amount and wouldn’t depend on aircraft, so costs and involved emissions would be relatively reduced.
The outcomes of particles on clouds are momentary and localized, so experiments on MCB could be carried out in excess of tiny places and transient time durations (probably spraying for a number of several hours for each working day in excess of quite a few months or months) without having severely perturbing the ecosystem or worldwide local climate. These tiny experiments would nevertheless yield major info on the impacts of brightening. What is far more, we can rapidly halt the use of MCB, with extremely fast cessation of its outcomes.
Solar local climate intervention is the umbrella time period for assignments that entail reflecting sunlight to cut down worldwide warming and its most perilous impacts.
Our project encompasses a few significant places of investigate. Initial, we require to obtain out if we can reliably and predictably improve reflectivity. To this close, we are going to require to quantify how the addition of produced sea salt particles alterations the variety of droplets in these clouds, and analyze how clouds behave when they have far more droplets. Relying on atmospheric ailments, MCB could affect items like cloud droplet evaporation price, the chance of precipitation, and cloud life span. Quantifying these types of outcomes will require equally simulations and discipline experiments.
Second, we require far more modeling to realize how MCB would affect weather conditions and local climate equally regionally and globally. It will be crucial to analyze any damaging unintended repercussions using correct simulations in advance of anybody considers implementation. Our team is initially focusing on modeling how clouds react to additional CCN. At some point we are going to have to verify our operate with tiny-scale discipline experiments, which will in transform improve the regional and worldwide simulations we are going to operate to realize the opportunity impacts of MCB under distinct local climate transform situations.
The third significant spot of investigate is the improvement of a spray procedure that can produce the size and concentration of particles essential for the initially tiny-scale discipline experiments. We are going to describe under how we’re tackling that problem.
1 of the initially measures in our project was to identify the clouds most amenable to brightening. Through modeling and observational experiments, we determined that the ideal concentrate on is stratocumulus clouds, which are reduced altitude (all around one to 2 km) and shallow we’re specially interested in “clean up” stratocumulus, which have reduced quantities of CCN. The improve in cloud albedo with the addition of CCN is frequently powerful in these clouds, whereas in further and far more hugely convective clouds other processes determine their brightness. Clouds in excess of the ocean are inclined to be clean up stratocumulus clouds, which is fortuitous, simply because brightening clouds in excess of dark surfaces, these types of as the ocean, will yield the highest albedo transform. They’re also conveniently close to the liquid we want to spray.
In the phenomenon identified as the Twomey influence, clouds with increased concentrations of tiny particles have a increased albedo, that means they are far more reflective. This kind of clouds could possibly be much less likely to produce rain, and the retained cloud water would retain albedo substantial. On the other hand, if dry air from previously mentioned the cloud mixes in (entrainment), the cloud may produce rain and have a decrease albedo. The total influence of MCB will be the mix of the Twomey influence and these cloud changes. Rob Wooden
Dependent on our cloud sort, we can estimate the variety of particles to produce to see a measurable transform in albedo. Our calculation includes the normal aerosol concentrations in clean up maritime stratocumulus clouds and the improve in CCN concentration essential to optimize the cloud brightening influence, which we estimate at 300 to four hundred for each cubic centimeter. We also take into account the dynamics of this portion of the ambiance, identified as the maritime boundary layer, thinking about equally the layer’s depth and the roughly a few-working day lifespan of particles within just it. Supplied all individuals aspects, we estimate that a solitary spray procedure would require to continually deliver somewhere around 3×10
15 particles for each 2nd to a cloud layer that addresses about 2,000 sq. kilometers. Considering that it’s likely that not every particle will access the clouds, we should aim for an buy or two bigger.
We can also determine the excellent particle size primarily based on first cloud modeling experiments and effectiveness issues. These experiments suggest that the spray procedure needs to produce seawater droplets that will dry to salt crystals of just 30–100 nanometers in diameter. Any lesser than that and the particles will not act as CCN. Particles much larger than a couple hundred nanometers are nevertheless productive, but their much larger mass implies that power is wasted in developing them. And particles that are considerably much larger than quite a few hundred nanometers can have a damaging influence, due to the fact they can trigger rainfall that benefits in cloud decline.
We require a apparent knowing of equally the efficacy and hazards of solar local climate intervention systems so individuals can make educated decisions about whether to employ them.
Generating dry salt crystals of the ideal size requires spraying seawater droplets of 120–400 nm in diameter, which is incredibly tough to do in an power-economical way. Regular spray nozzles, exactly where water is compelled by a slim orifice, produce mists with diameters from tens of micrometers to quite a few millimeters. To lower the droplet size by a factor of ten, the tension by the nozzle must improve far more than 2,000 instances. Other atomizers, like the ultrasonic nebulizers uncovered in dwelling humidifiers, equally can’t produce tiny sufficient droplets without having exceptionally substantial frequencies and energy specifications.
Fixing this difficulty required equally out-of-the-box pondering and abilities in the manufacturing of tiny particles. That’s exactly where
Armand Neukermans came in.
After a distinguished occupation at HP and Xerox concentrated on manufacturing of toner particles and ink jet printers, in 2009 Neukermans was approached by quite a few eminent local climate researchers, who requested him to transform his abilities toward generating seawater droplets. He rapidly assembled a cadre of volunteers—mostly retired engineers and researchers. and in excess of the upcoming decade, these self-selected “Outdated Salts” tackled the problem. They worked in a borrowed Silicon Valley laboratory, using gear scrounged from their garages or purchased out of their possess pockets. They explored quite a few strategies of producing the ideal particle size distributions with various tradeoffs concerning particle size, power effectiveness, technical complexity, reliability, and price tag. In 2019 they moved into a lab place at PARC, exactly where they have accessibility to gear, products, amenities, and far more researchers with abilities in aerosols, fluid dynamics, microfabrication, and electronics.
The a few most promising methods discovered by the team have been effervescent spray nozzles, spraying salt water under supercritical ailments, and electrospraying to kind Taylor cones (which we are going to describe afterwards). The initially choice was considered the easiest to scale up rapidly, so the team moved forward with it. In an effervescent nozzle, pressurized air and salt water are pumped into a solitary channel, exactly where the air flows by the middle and the water swirls all around the sides. When the mixture exits the nozzle, it makes droplets with sizes ranging from tens of nanometers to a number of micrometers, with the overpowering variety of particles in our ideal size variety. Effervescent nozzles are employed in a variety of programs, which includes engines, gas turbines, and spray coatings.
The important to this technologies lies in the compressibility of air. As a gas flows by a constricted place, its velocity boosts as the ratio of the upstream to downstream pressures boosts. This marriage holds until finally the gas velocity reaches the velocity of seem. As the compressed air leaves the nozzle at sonic speeds and enters the ecosystem, which is at much decrease tension, the air undergoes a fast radial enlargement that explodes the bordering ring of water into very small droplets.
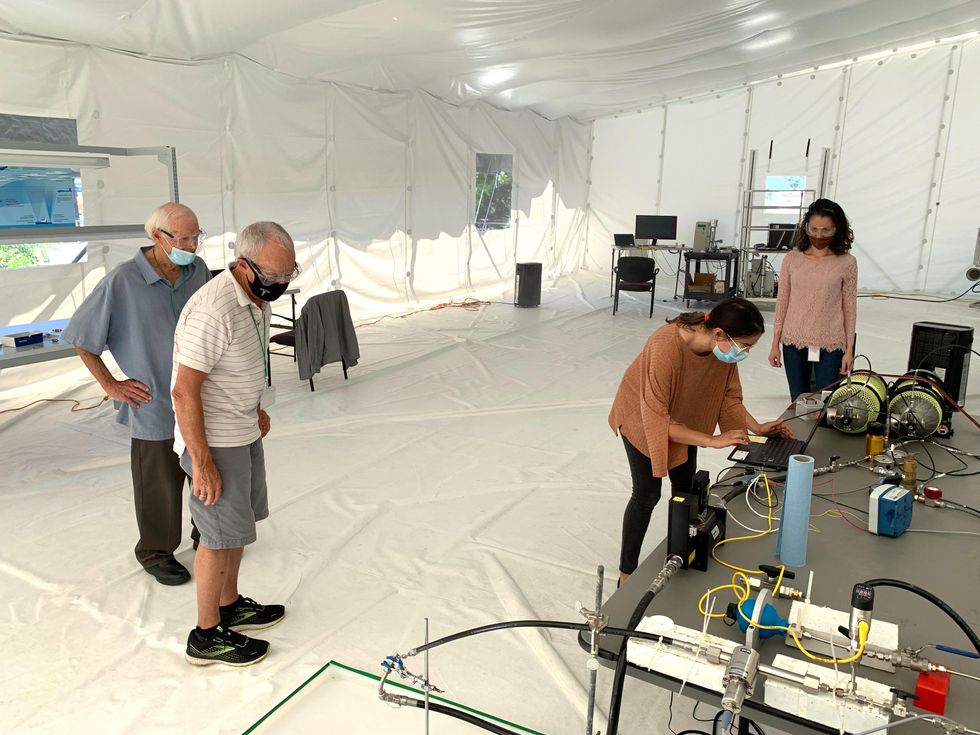
Coauthor Gary Cooper and intern Jessica Medrado check the effervescent nozzle inside of the tent. Kate Murphy
Neukermans and company uncovered that the effervescent nozzle performs nicely sufficient for tiny-scale screening, but the efficiency—the power required for each correctly sized droplet—still needs to be improved. The two major resources of waste in our procedure are the big quantities of compressed air essential and the big fraction of droplets that are as well big. Our newest initiatives have concentrated on redesigning the move paths in the nozzle to require lesser volumes of air. We are also performing to filter out the big droplets that could trigger rainfall. And to improve the distribution of droplet size, we’re thinking about strategies to incorporate charge to the droplets the repulsion concerning charged droplets would inhibit coalescence, lowering the variety of outsized droplets.
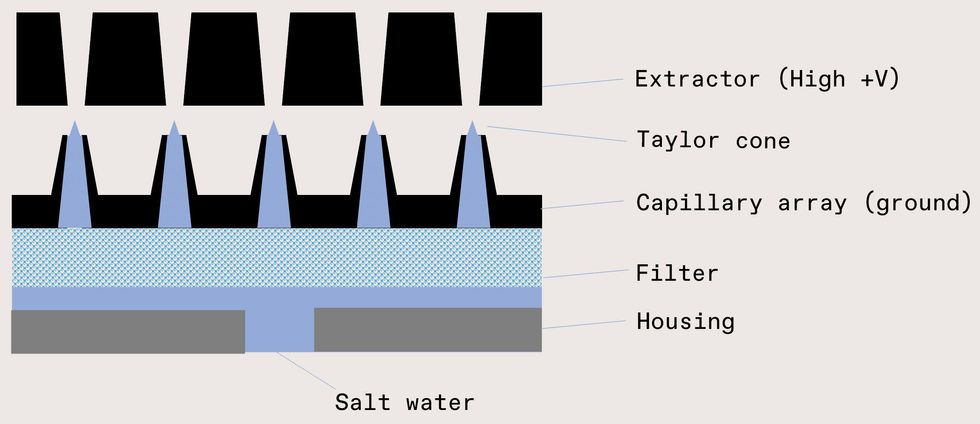
However we’re generating progress with the effervescent nozzle, it in no way hurts to have a backup prepare. And so we’re also checking out electrospray technologies, which could yield a spray in which almost 100 per cent of the droplets are within just the ideal size variety. In this strategy, seawater is fed by an emitter—a slim orifice or capillary—while an extractor makes a big electrical discipline. If the electrical pressure is of equivalent magnitude to the area stress of the water, the liquid deforms into a cone, normally referred to as a Taylor cone. Above some threshold voltage, the cone suggestion emits a jet that rapidly breaks up into hugely charged droplets. The droplets divide until finally they access their Rayleigh restrict, the point exactly where charge repulsion balances the area stress. Fortuitously, area seawater’s normal conductivity (4 Siemens for each meter) and area stress (73 millinewtons for each meter) yield droplets in our ideal size variety. The final droplet size can even be tuned by means of the electrical discipline down to tens of nanometers, with a tighter size distribution than we get from mechanical nozzles.
This diagram (not to scale) depicts the electrospray procedure, which makes use of an electrical discipline to develop cones of water that crack up into very small droplets. Kate Murphy
Electrospray is relatively very simple to reveal with a solitary emitter-extractor pair, but a person emitter only makes 10
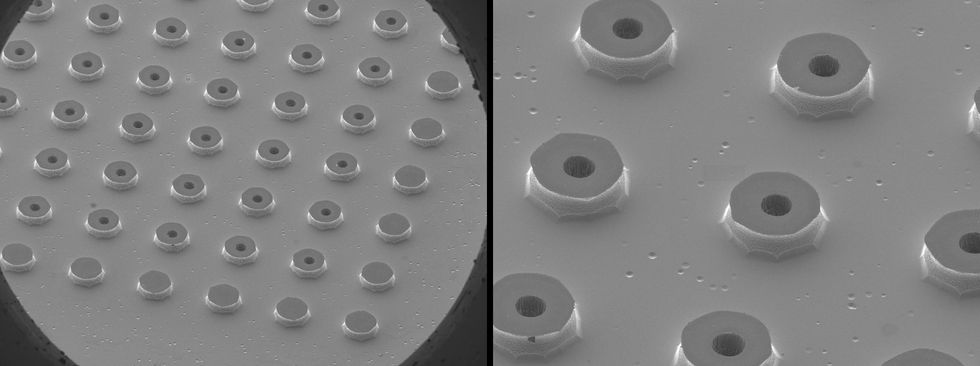
7–109 droplets for each 2nd, whereas we require 1016–10seventeen for each 2nd. Manufacturing that total requires an array of up to 100,000 by 100,000 capillaries. Creating these types of an array is no tiny feat. We are relying on methods far more frequently involved with cloud computing than actual clouds. Employing the exact same lithography, etch, and deposition methods employed to make built-in circuits, we can fabricate big arrays of very small capillaries with aligned extractors and exactly positioned electrodes.
Visuals taken by a scanning electron microscope display the capillary emitters employed in the electrospray procedure. Kate Murphy
Screening our systems provides nevertheless one more set of issues. Ideally, we would like to know the first size distribution of the saltwater droplets. In practice, which is approximately difficult to measure. Most of our droplets are lesser than the wavelength of light-weight, precluding non-make contact with measurements primarily based on light-weight scattering. Alternatively, we must measure particle sizes downstream, immediately after the plume has progressed. Our key software, identified as a
scanning electrical mobility spectrometer, steps the mobility of charged dry particles in an electrical discipline to determine their diameter. But that process is sensitive to aspects like the room’s size and air currents and whether the particles collide with objects in the place.
To address these difficulties, we developed a sealed 425 cubic meter tent, outfitted with dehumidifiers, fans, filters, and an array of linked sensors. Doing work in the tent will allow us to spray for more time durations of time and with multiple nozzles, without having the particle concentration or humidity turning out to be increased than what we would see in the discipline. We can also analyze how the spray plumes from multiple nozzles interact and evolve in excess of time. What is far more, we can far more exactly mimic ailments in excess of the ocean and tune parameters these types of as air velocity and humidity.
Component of the team inside of the check tent from remaining, “Outdated Salts” Lee Galbraith and Gary Cooper, Kate Murphy of PARC, and intern Jessica Medrado. Kate Murphy
We are going to at some point outgrow the tent and have to move to a big indoor place to proceed our screening. The upcoming stage will be outdoor screening to analyze plume habits in true ailments, though not at a substantial sufficient price that we would measurably perturb the clouds. We might like to measure particle size and concentrations far downstream of our sprayer, from hundreds of meters to quite a few kilometers, to determine if the particles carry or sink and how far they distribute. This kind of experiments will support us optimize our technologies, answering these types of inquiries as whether we require to incorporate warmth to our procedure to persuade the particles to increase to the cloud layer.
The facts received in these preliminary checks will also inform our styles. And if the benefits of the design experiments are promising, we can continue to discipline experiments in which clouds are brightened sufficiently to analyze important processes. As talked about previously mentioned, these types of experiments would be carried out in excess of a tiny and shorter time so that any outcomes on local climate wouldn’t be major. These experiments would supply a significant verify of our simulations, and as a result of our capability to accurately predict the impacts of MCB.
It can be nevertheless unclear whether MCB could support culture steer clear of the worst impacts of local climate transform, or whether it’s as well risky, or not productive sufficient to be beneficial. At this point, we you should not know sufficient to advocate for its implementation, and we’re certainly not suggesting it as an alternate to reducing emissions. The intent of our investigate is to supply policymakers and culture with the facts essential to assess MCB as a person strategy to gradual warming, delivering info on equally its opportunity and hazards. To this close, we have submitted our experimental strategies for evaluation by the
U.S. Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and for open up publication as portion of a U.S. Nationwide Academy of Sciences analyze of investigate in the discipline of solar local climate intervention. We hope that we can get rid of light-weight on the feasibility of MCB as a software to make the world safer.
From Your Site Articles or blog posts
Relevant Articles or blog posts All over the World wide web